What Are Piles? And it's Treatment in Homeopathic
Hemorrhoids, often referred to as piles, are a widespread ailment that affects millions of individuals globally. Despite being common, there is frequently a dearth of awareness and comprehension regarding this condition. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, types, and symptoms of hemorrhoids to offer clarity and valuable insights for individuals grappling with this uncomfortable concern.
What are hemorrhoids?
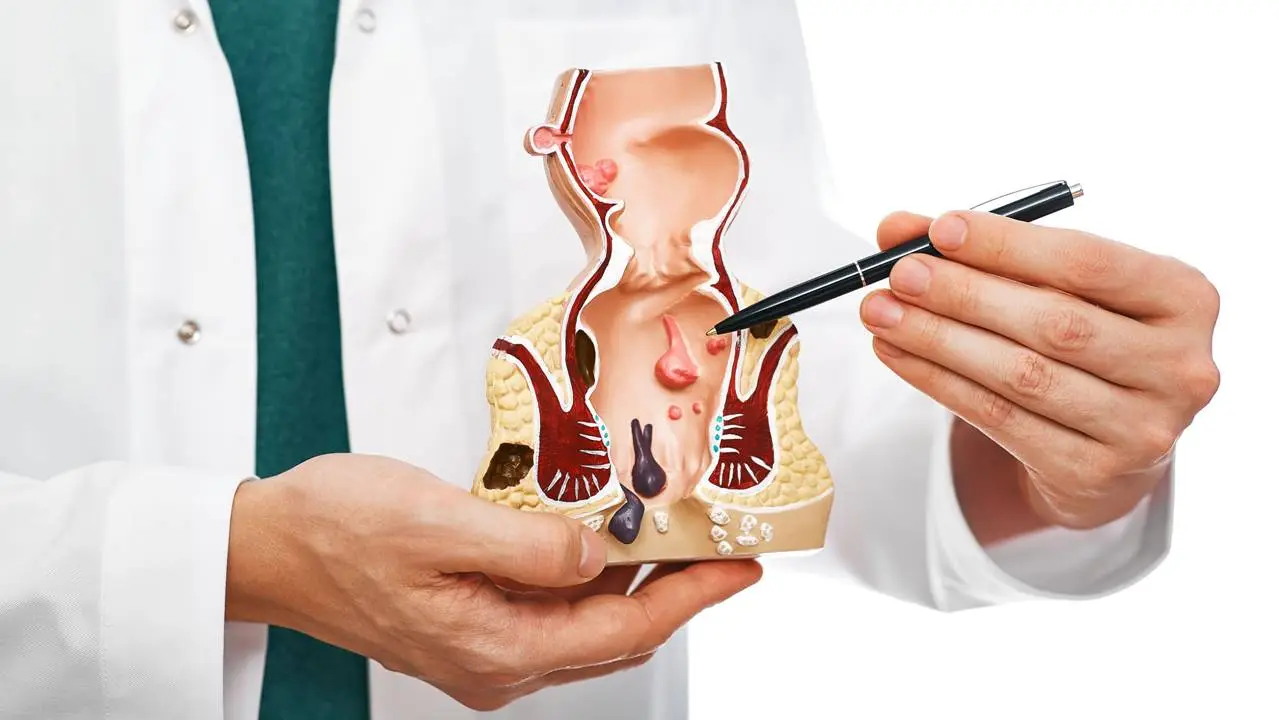
Hemorrhoids are enlarged veins found in the lower rectum or anus. These veins may swell and become inflamed due to various factors, causing discomfort, pain, and occasionally bleeding.
Types of piles (Hemorrhoids):
There are two main types of hemorrhoids:
- Internal Hemorrhoids: These are situated inside the rectum and usually do not cause pain. However, they may result in bleeding during bowel movements.
- External Hemorrhoids: These develop beneath the skin around the anus. They can be painful and often lead to itching and irritation.
Hemorrhoids are typically graded based on their severity, aiding in determining the appropriate treatment approach.
The commonly used grading system for hemorrhoids is as follows:
- Grade I: Hemorrhoids that bleed but do not prolapse (come out of the anal canal) are categorized as Grade I hemorrhoids. They may cause painless bleeding during bowel movements.
- Grade II: These hemorrhoids prolapse during a bowel movement but retract spontaneously. They may result in bleeding and discomfort.
- Grade III: Hemorrhoids that prolapse during a bowel movement and necessitate manual manipulation. They may cause bleeding, discomfort, and protrusion outside the anus.
- Grade IV: Representing the most severe form of hemorrhoids, Grade IV hemorrhoids are prolapsed and cannot be pushed back inside the anal canal. They may lead to significant pain, bleeding, and difficulties with hygiene.
Causes of Hemorrhoids:
- Hemorrhoids can arise due to various factors such as:
Excessive straining during bowel movements. - Chronic constipation or diarrhea.
- Prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
- Obesity or being overweight.
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Aging, which leads to the weakening of tissues supporting the veins in the rectum and anus.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids:
The symptoms of hemorrhoids can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Below are some symptoms associated with piles that you should be aware of:
Anal itching: Hemorrhoids can lead to significant itching around the anus, particularly if they are external.
Swelling: The presence of swelling, which manifests as small balloon-like swellings in the anal area, is a common sign of hemorrhoids and can cause tenderness in the anus.
Anal pain: External piles often result in pain in the anal region, making bowel movements and sitting uncomfortable.
Bleeding: The passage of blood with stools can indicate the presence of internal piles.
Lumps near the anus: The appearance of lumps on the anal surface, which may feel hard or tender, is a notable symptom of piles.
Slimy anal discharge: An anal discharge that is slimy in nature can lead to staining of underwear or may be passed along with stool.
Sore skin on the anus: Soreness of the skin around the anus or protruding skin after bowel movements is typically associated with hemorrhoids.
Complications:
Complications linked with hemorrhoids, also known as piles, encompass a range of potential issues arising from the inflammation, swelling, and enlargement of blood vessels in the anal canal. These complications may include:
- Thrombosis: This occurs when a blood clot forms within the swollen hemorrhoidal veins, resulting in severe pain, inflammation, and a palpable lump near the anus.
- Bleeding: Hemorrhoids can cause bleeding during bowel movements, leading to bright red blood in the stool or on toilet paper. Persistent bleeding can lead to anemia over time.
- Prolapse: In advanced cases, internal hemorrhoids may protrude outside the anal opening, causing discomfort, pain, and hygiene difficulties. Prolapsed hemorrhoids may require manual reduction or medical intervention.
- Strangulation: When internal hemorrhoids prolapse and become trapped outside the anus, they may lose their blood supply, leading to tissue necrosis. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
- Infection: Hemorrhoids can become infected due to scratching, irritation, or poor hygiene, resulting in symptoms such as fever, swelling, redness, and pus discharge. In severe cases, abscess formation may occur.
- Fissures and Fistulas: Chronic straining and irritation linked with hemorrhoids can lead to the development of anal fissures (tears in the anal lining) or fistulas (abnormal tunnels between the anus and nearby skin), causing pain, bleeding, and infection.
- Chronic Pain and Discomfort: Persistent discomfort, itching, burning, and pain can significantly impair quality of life and interfere with daily activities, leading to psychological distress and decreased productivity.
- Anemia: Chronic bleeding from hemorrhoids can result in iron deficiency anemia, characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Precautions for piles:
Precautions for piles (also known as hemorrhoids) can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Here are some general precautions to consider:
- Maintain a High-Fiber Diet: Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can aid in softening stools, making them easier to pass, and reducing strain during bowel movements.
- Stay Hydrated: Ensure adequate hydration by drinking plenty of water, as it helps in keeping stools soft, facilitating easier passage and lowering the risk of constipation.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation, which can exacerbate hemorrhoids.
- Avoid Straining: Refrain from straining during bowel movements, as it can worsen hemorrhoids. Take your time in the bathroom and avoid excessive pushing.
- Don’t Delay Bowel Movements: Respond promptly to the urge to have a bowel movement to prevent constipation and further aggravation of hemorrhoids.
- Practice Good Anal Hygiene: After bowel movements, gently cleanse the anal area with water or unscented, alcohol-free wipes to prevent irritation, avoiding rough toilet paper.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Minimize prolonged periods of sitting or standing to alleviate pressure on the anal area, which can worsen hemorrhoid symptoms. Take breaks and change positions regularly.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Reduce strain on the abdominal and pelvic muscles by avoiding heavy lifting whenever possible, as it can increase pressure on the veins in the rectal area.
- Manage Weight: Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to lower the risk of developing hemorrhoids, as obesity and excess weight can increase susceptibility to this condition.
How to treat piles without surgery?
Warsan Homeopathic’s Hemokit (Piles Cure Capsules) is a non-surgical treatment for piles and fissures, offering an alternative approach to addressing hemorrhoids. It aims to effectively manage hemorrhoidal symptoms without the need for invasive surgery. This therapeutic solution is crafted with a blend of natural ingredients and advanced formulations, intending to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of hemorrhoidal tissues caused by constipation-related fissures.
Recognized as the top choice for hemorrhoid relief, Hemokit stands out for its proven effectiveness, natural composition, and commitment to quality, making it the preferred option for individuals seeking optimal relief from hemorrhoidal discomfort without resorting to surgical intervention.
Choosing Premium Supplements from Warsan Homeopathic
At Warsan Homeopathic, we’re committed to providing men with premium-quality best vitamin supplements for men that address their unique health needs. Our extensive range of vitamin and herbal formulations undergoes strict quality control measures to ensure purity, potency, and safety. Whether you’re looking to support muscle health, boost cardiovascular function, enhance cognitive performance, or improve sexual vitality, we have a solution for you. With Warsan Homeopathic, you can trust that you’re investing in your health and well-being.