Eczema Treatment In Homeopathy
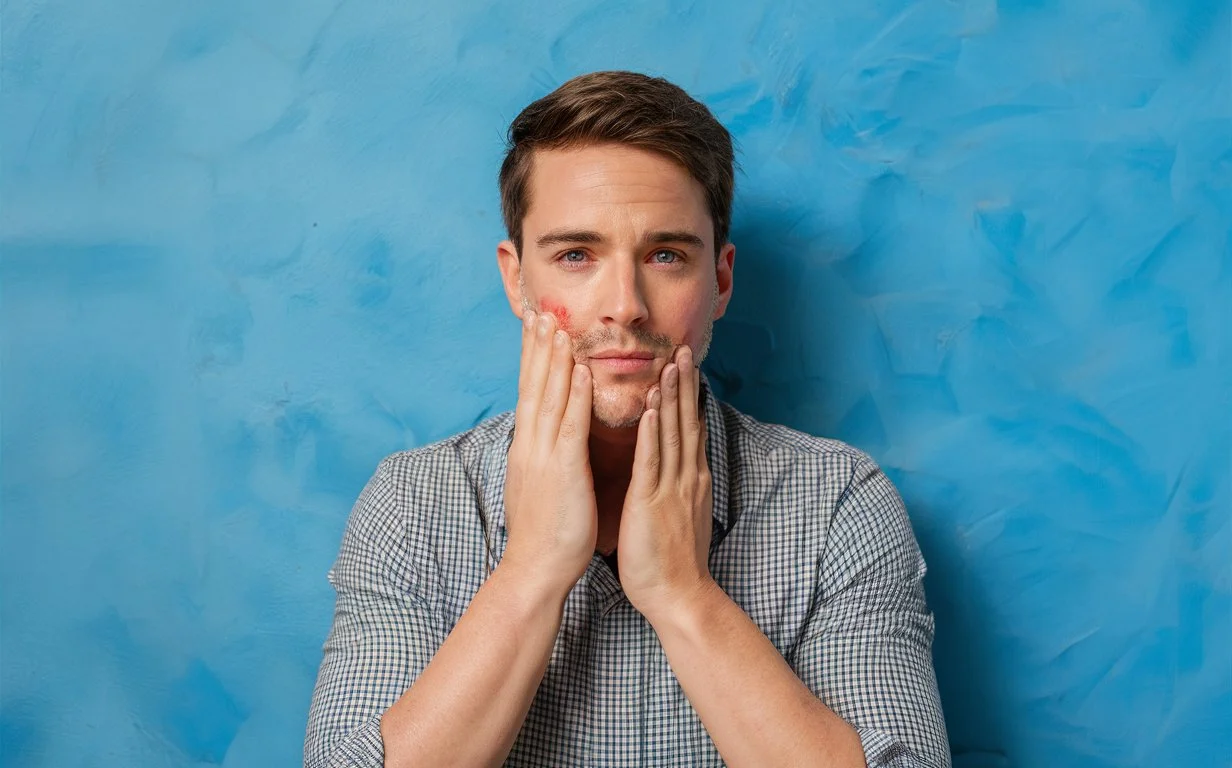
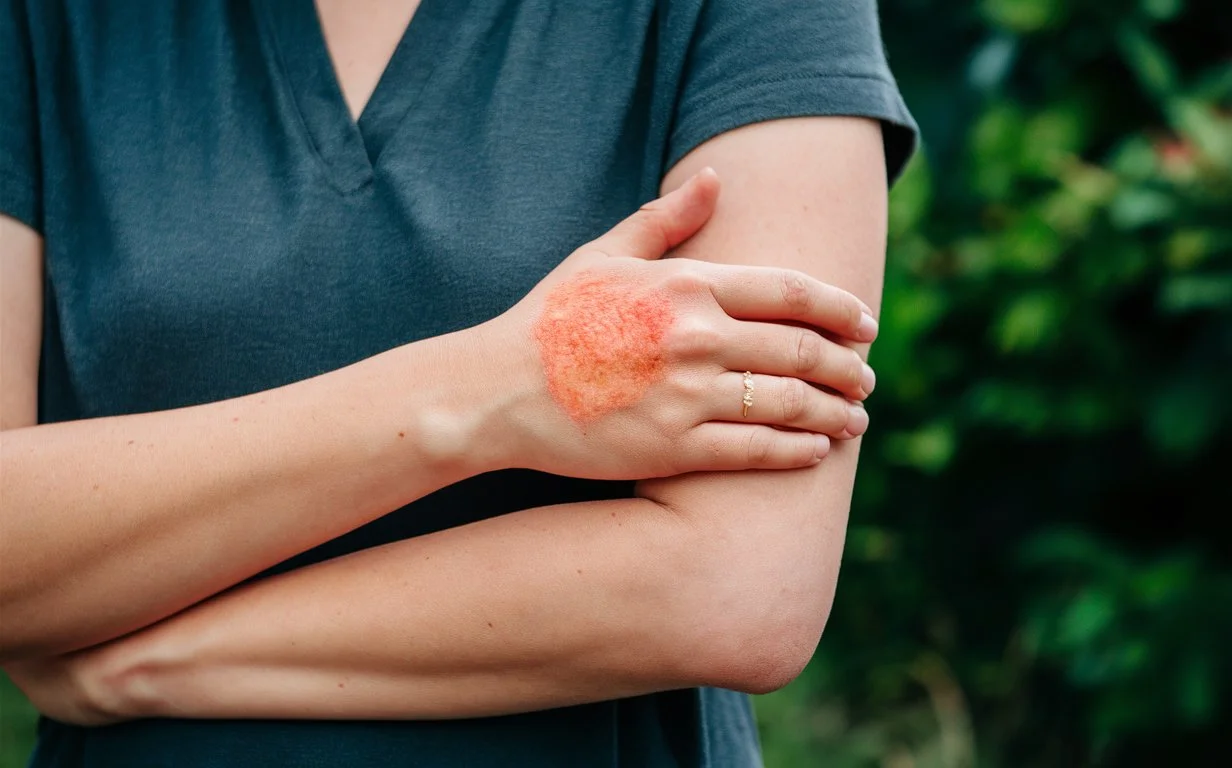
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition marked by inflammation, redness, itching, and occasionally the development of small fluid-filled blisters. It’s a prevalent condition that typically manifests in childhood and may continue into adulthood.
Eczema usually doesn’t cause pain, but scratching the affected skin can break the skin’s surface, resulting in the formation of sores that may cause discomfort.
Types:
Here are some of the main types of eczema:
Atopic dermatitis: This variant represents the most prevalent manifestation of eczema, often initiating in childhood and persisting into adulthood. Characterized by parched, pruritic, inflamed skin, it tends to exhibit familial aggregation, particularly in lineages with a history of asthma, hay fever, or eczema.
Contact dermatitis: This subtype arises upon contact with an irritant or allergen, eliciting erythema, pruritus, and occasionally vesiculation.
Dyshidrotic eczema: Also recognized as pompholyx eczema, this form primarily targets the palmar surfaces, plantar regions, and lateral aspects of the digits, resulting in vesicular eruptions and intense pruritus. While its precise etiology remains elusive, plausible factors include stress, allergens, or exposure to specific metals.
Nummular eczema: Distinguished by circular or oval lesions of inflamed, pruritic epidermis prone to exudation or crusting, this variant is frequently precipitated by xerosis, irritants, or climatic influences such as cold temperatures.
Seborrheic dermatitis: Predominantly affecting areas rich in sebaceous glands such as the scalp, facial region (particularly periocular, nasal, and auricular regions), and upper thorax, this form manifests as erythematous, sebaceous skin adorned with yellowish or whitish scales. Provocative elements may include stressors, hormonal imbalances, or dysregulated cutaneous yeast proliferation.
Stasis dermatitis: Commonly observed in the lower extremities, notably among individuals afflicted with compromised vascular perfusion or venous insufficiency, this presentation is typified by edema, erythema, and desquamation, often accompanied by pruritus and discomfort.
Causes:
The precise cause of eczema remains uncertain according to experts. However, factors that could heighten the likelihood of its occurrence include:
- Immune system sensitivity provoked by irritants.
- Impaired resilience of the skin’s protective barrier, promoting moisture depletion and microbial infiltration.
- Genetic inclination associated with a familial background of allergies or asthma.
Eczema symptoms:
Dry skin: Eczema often results in skin becoming parched, coarse, and flaky.
Itching (pruritus): Intense itching is a hallmark symptom of eczema, which can be severe and lead to scratching, exacerbating skin irritation.
Redness (erythema): Affected skin areas may display redness or inflammation due to irritation and inflammation.
Inflammation: Eczema can induce skin swelling, tenderness, and heightened sensitivity to touch.
Rash: Eczema frequently generates a rash, exhibiting various appearances depending on the eczema type. It may manifest as small bumps, blisters, patches of redness, or dry, scaly regions.
Cracking and oozing: In certain instances, eczema can cause skin to fissure or exude fluid, especially when severely irritated or infected.
Thickened skin (lichenification): Persistent scratching and rubbing of the skin can result in thickened and toughened skin, termed lichenification.
Discoloration: Over time, eczema may lead to skin discoloration, appearing darker or lighter compared to adjacent skin.
Pain or discomfort: In severe cases, eczema can induce pain or discomfort, particularly if the skin becomes fissured or infected.
Eczema risk factors:
- Genetic predisposition: A familial background of eczema, allergies, or asthma can elevate the risk of developing the condition.
- Environmental triggers: Contact with specific irritants, allergens, or pollutants can worsen or initiate eczema episodes.
- Skin barrier dysfunction: Structural irregularities or impairment of the skin’s protective barrier can heighten its vulnerability to inflammation and irritation.
Homeopathic treatment:
Homeopathic treatment for eczema follows the principle of “like cures like” and is tailored to each individual’s symptoms and constitution. In a homeopathic consultation, the practitioner evaluates not only the physical manifestations of eczema but also the person’s emotional and mental well-being, lifestyle, and any underlying health issues.
Homeopathic remedies for eczema may encompass substances such as Graphites, Sulphur, Arsenicum album, or Petroleum, among others, chosen based on the distinctive symptoms and features of the eczematous eruptions.
Choosing Premium Supplements from Warsan Homeopathic
Choosing premium supplements from Warsan Homeopathic ensures you’re investing in top-quality products crafted to enhance your health and well-being. Our extensive range of vitamin and herbal formulations undergoes rigorous quality control measures to guarantee purity, potency, and safety. Whether you’re seeking to support muscle health, boost cardiovascular function, enhance cognitive performance, or improve sexual vitality, we have a solution tailored to your needs. Trust Warsan Homeopathic to provide you with the best in natural supplementation for optimal health outcomes.